Description
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is a member of the CD28 superfamily and is a negative regulator of T cell-mediated immune responses. CTLA-4 expression is induced on the surface of T cells after CD28 binding and activation, and is constitutively expressed on T-regulatory cells, acting as an immune checkpoint inhibitor, downregulating T cell activity. (1-3). CTLA-4 primarily inactivates T-cell activity by competing with the CD28 costimulatory molecule (1,3). CD28 and CTLA-4 share the identical ligands of CD80 and CD86 on antigenpresenting cells; and thus CTLA-4 competes with CD28 function in T-cell survival, proliferation, and recruitment (3,4). In particular, CTLA-4 down-modulates CD4+ helper T-cell activity and enhances Treg immunosuppressive functions (5).
CTLA-4 has been shown to play a role in human diseases (1,3). CTLA-4 acts as a physiological brake on the activated immune system in order to maintain immune homeostasis. Several suppressive mechanisms for T-cell functions have been attributed to CTLA-4. FDA approved Ipilimumab (IgG1 isotype), a monoclonal antibody to CTLA-4, was the first immunotherapeutic drug directed toward CTLA-4 inhibition to demonstrate overall survival benefit in metastatic melanoma (1,6). Another CTLA-4 inhibitor, tremelimumab (IgG2 isotype), has also proven successful in metastatic melanoma and other malignancies (1,6).
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
|---|---|
| FORMAT | Concentrate, Predilute |
| VOLUME | 0.1 ml, 0.5 ml, 6.0 ml |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human and Mouse |
| SOURCE | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| CLONE | CAL49 |
| ISOTYPE | IgG1 |
| ANTIGEN | Synthetic peptide derived from a region of the CTLA-4 protein |
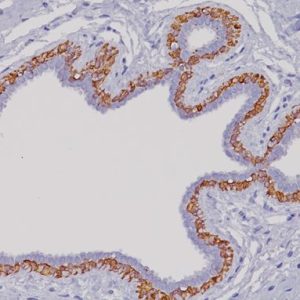
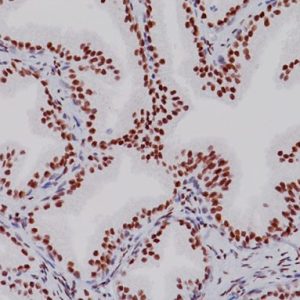
| LOCALIZATION | Membranous/cytoplasmic |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Tonsil |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Buchbinder EI, McDermott DF. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 blockade in melanoma. Clinical Therapeutics. 2015; 37:755-63.
2. Baecher-Allan C, et al. Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Semin Immunol. 2004 Apr; 16(2):89-98.
3. Scalapino KJ, Daikh DI. CTLA-4: a key regulatory point in the control of autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2008 Jun;223:143-55.
4. Schwartz RH. Costimulation of T lymphocytes: the role of CD28, CTLA-4, and B7/BB1 in interleukin-2 production and immunotherapy. Cell. 1992; 71:1065-8.
5. Wing K, et al. CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science. 2008; 322:271-5.
6. Shin DS, Ribas A. The evolution of checkpoint blockade as a cancer therapy: what’s here, what’s next? Curr Opin Immunol. 2015; 33:23-35.
7. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved Guideline-Fourth Edition CLSI document M29-A4 Wayne, PA 2014.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.