Description
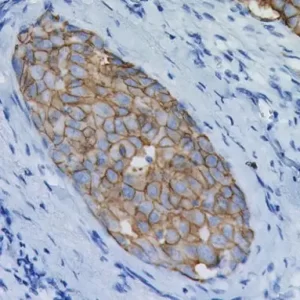
p53 homologue p63 encodes for different isotypes able to either transactivate p53 reporter genes (TAp63) or act as p53-dominant-negatives. Studies have shown that p63 [4a4] antibody detection by IHC has clinical utility in the evaluation of lung, prostate, cervical and other types of cancer in formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) human tissues. A cocktail of p63 and TRIM29 can also be utilized for lung SqCC and studies have shown that when p63 and/or TRIM29 is expressed in lung SqCC, a 95.4% sensitivity and 100% specificity was achieved, if Napsin A and TTF-1 were both negative in the same case.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| WEIGHT | N/A |
|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | N/A |
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| SOURCE | Mouse Monoclonal |
| CLONE | 4A4 |
| ISOTYPE | IgG2a/kappa |
| ANTIGEN | p63 |
| LOCALIZATION | Nuclear |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Normal prostate |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Yang A, et. al. p63, a p53 Homolog at 3q27–29, Encodes Multiple Products with Transactivating, Death-Inducing, and Dominant-Negative Activities. Mol Cell. 1998;2:305-16.
2. Signoretti S, et. al. p63 Is a Prostate Basal Cell Marker and Is Required for Prostate Development. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:1769-75.
3. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved guideline-Third Edition CLSI document M29-A3 Wayne, PA 2005.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.