Description
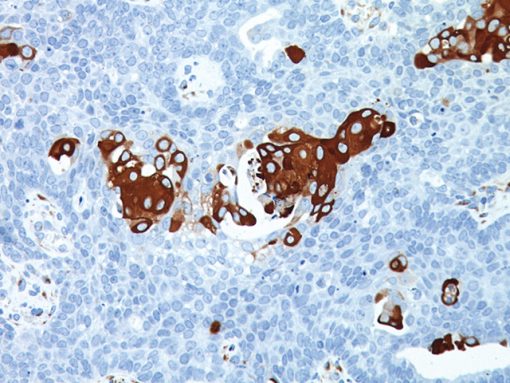
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a sub-family of growth factors, more specifically of platelet-derived growth factor family of cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature) (2-3). In certain cancers, high VEGF expression has been correlated with shorter survival (1).
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| WEIGHT | N/A |
|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | N/A |
| INTENDED USE | RUO |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human |
| SOURCE | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| CLONE | EP1176Y |
| ISOTYPE | IgG |
| ANTIGEN | VEGF |
| LOCALIZATION | Membrane and / or cytoplasmic |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Tonsil, some breast and ovarian cancers |
DATASHEETS & SDS
OUS ONLY IVD
REFERENCES
1. Saad RS, et al. Lymphatic microvessel density as prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Modern Pathol. 2006 Oct; 19(10):1317-23.
2. Lee AH, et al. Invasive lobular and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast show distinct patterns of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis. J Pathol. 1998 Aug; 185(4):394-401.
3. Applanat MP, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a target gene for estrogen receptor and contributes to breast cancer progression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008; 617:437-44.
4. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory workers from occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved guideline-Third Edition CLSI document M29-A3 Wayne, PA 2005.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.